Content

Businesses with international operations must translate their transactions like the acquisition of assets or the purchase of services into their functional currency. With foreign exchange fluctuations, the value of these assets and liabilities are also subject to variations. It is vital that you keep a close eye on the dates in which any of the above transactions occurred.
Additional accounts may be added, but any change to the lines or columns will require that the equations be altered accordingly. Although the worksheets use the current rate method, they can be adapted to another translation method. When corporate earnings growth was in the double digits in 2006, favorable foreign currency translation was only a small part of the earnings story. But now, in a season of lower earnings coupled with volatility in currency exchange rates, currency translation gains represent a far greater portion of the total. IAS 21 is silent on which part of P&L should foreign exchange differences be presented in.
Under IFRS, the foreign currency statements are first restated for local inflation and then translated using the current exchange rate. Under US GAAP, the foreign currency financial statements Foreign Currency Translation are translated using the temporal method, with no restatement for inflation. The prices at which foreign currencies can be purchased or sold are called foreign exchange rates.
Remeasurement And Translation
Under this method, nonmonetary balance sheet accounts and related income statement accounts are re-measured using historical exchange rates. The remeasurement process should produce the same result as if the entity’s accounting records had been maintained in the functional currency.
- The indirect rate is the number of units of the foreign currency that can be purchased for one U.S. dollar.
- The reduction in capital risk through the use of FX forwards is accompanied by an increase in liquidity risk.
- When these indicators are mixed, priority is given to the primary indicators listed in paragraph IAS 21.9.
- Service provision within the BDO network in connection with IFRS , and other documents, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, is provided by BDO IFR Advisory Limited, a UK registered company limited by guarantee.
- Others choose to enter into instruments such as foreign exchange forward contracts, foreign exchange option contracts and foreign exchange swaps.
- The entity does not reclassify within equity the cumulative pre-hyperinflation exchange differences once the foreign operation becomes hyperinflationary.
- The GAAP regulations require the items in the balance sheet be converted in accordance with the rate of exchange as on the date of balance sheet while the income statement items are converted according to the weighted average rate of exchange.
When several exchange rates are available, the rate used is that at which the future cash flows represented by the transaction or balance could have been settled if those cash flows had occurred at the measurement date (IAS 21.26). IAS 21 allows application of simplifications in determining the foreign exchange rate, e.g. by using an average rate, provided that exchange rates do not fluctuate significantly (IAS 21.22). In practice, entities most often use the average of monthly rates, as these are usually published by central banks for most currencies.
The Regulatory Framework And Presentation Of Financial Statements
The Group recognizes the net obligation of a defined benefit plan in its Balance Sheet as an asset or liability, respectively in accordance with IAS 19, Employee benefits. Actuarial gains and losses arising from experience adjustments and changes in actuarial assumptions are charged or credited to net profit in the statement of comprehensive income in the period in which they arise. When the computation results in a benefit to the Group, the recognized asset is limited to the net total of any unrecognized past service costs and the present value of any future refunds from the plan or reductions in future contributions to the plan. Goodwill and fair value adjustments arising on the acquisition of a foreign entity are treated as assets and liabilities of the foreign entity and translated at the exchange rate in effect at the Balance Sheet date. How money from one country is valued in another informs many different business decisions, from the timing of imports and exports to the locations of overseas offices. Daily changes are usually minimal, but depending on how much money is at stake, even the smallest change can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line. Accurate and uniform foreign currency translation practices are accordingly very important.

According to FASB Rule 52, you also apply the temporal rate method if you operate in a hyperinflationary environment. The accounting standards’ methodologies employ the functional currency translation approach, which relies on the current rate method when the functional currency is the same as the local currency – for example, a London subsidiary using the British pound. In the current rate method, assets and liabilities use the current, or “spot,” exchange rate existing on the date of translation – the date on the balance sheet. If the functional currency of the subsidiary is not its home currency, the temporal method is used.
Foreign Currency Translation Methods
Even if you have a QBU, your functional currency is the dollar if any of the following apply. Note that this Roadmap is not a substitute for the exercise of professional judgment, which is often essential to applying the requirements of ASC 830. It is also not a substitute for consulting with Deloitte professionals on complex accounting questions and transactions. This Roadmap provides Deloitte’s insights into and interpretations of the accounting guidance under ASC 830 and IFRS® Standards.
ASC 830 is not a standard, but rather where all the previous standards dealing with foreign currency have been «codified» into a single topic. For example FASB Statement No. 52 «https://www.bookstime.com/» was issued in December 1981 and its guidance is still applicable . Therefore, the functional currency of Rotor would be Copter’s functional currency, the Australian dollar . An analyst can obtain information about the tax impact of multinational operations from companies’ disclosure on effective tax rates. “EisnerAmper” is the brand name under which EisnerAmper LLP and Eisner Advisory Group LLC, independently owned entities, provide professional services in an alternative practice structure in accordance with applicable professional standards. EisnerAmper LLP is a licensed CPA firm that provides attest services, and Eisner Advisory Group LLC and its subsidiary entities provide tax and business consulting services. Cohen & Company is not rendering legal, accounting or other professional advice.
Foreign Currency And Currency Exchange Rates
Adjustments resulting from the remeasurement process are generally recorded in net income. The specific rules governing how foreign currency translation must be conducted are usually a matter of national law. Laws usually stipulate the calendar date that companies must use to determine the relevant exchange rate, for instance, and set out specific rules to be followed in compiling consolidated financial statements. Rules for reporting currency fluctuations and deviations are also frequently included. If a balance sheet date falls between the transaction date and the settlement date, the foreign currency account receivable is translated at the exchange rate at the balance sheet date. The change in the functional currency value of the foreign currency account receivable is recognized as a foreign currency transaction gain or loss in income.
- Currency translation is largely a matter of converting the functional currency into the presentation currency.
- Companies with overseas operations often choose to publish reported numbers alongside figures that strip out the effects of exchange rate fluctuations.
- How an entity applies the requirements in paragraph 48D is largely dependent on whether it interprets ‘any reduction in an entity’s ownership interest in a foreign operation’ to mean an absolute reduction, a proportionate reduction, or both.
- Exchange differences arising from the translation of a foreign operation previously recognised in other comprehensive income are not reclassified from equity to profit and loss until the disposal of the operation.
An accounting term meaning that one currency is restated in terms of another currency is called foreign currency translation. The effect of changes in tax rates on deferred income tax assets and liabilities is recognized as income or expense in the period that includes the enactment or the substantive enactment date. Very often, the application of points and above to gaming entities, does not give a straightforward interpretation of what that gaming entity’s functional currency is. This is because a company with a gaming licence in a specific country, would have the facility to operate in several different jurisdictions, which could result in having revenues denominated in various currencies. The functional currency may differ from the “local” currency, which is the official currency of a nation. Parent companies use the “presentation” currency for financial reporting – it’s normally the home currency.
The Committee has not obtained evidence that a project with that scope—undertaken in isolation of other aspects of the accounting for hyperinflationary foreign operations—would result in an improvement in financial reporting that would be sufficient to outweigh the costs. Consequently, the Committee decided not to add the matter to its standard-setting agenda. Paragraph 8 of IAS 21 defines the ‘closing rate’ as the spot exchange rate at the end of the reporting period; and the ‘spot exchange rate’ as the exchange rate for immediate delivery. In the light of those definitions, the Committee concluded that the closing rate is the rate to which an entity would have access at the end of the reporting period through a legal exchange mechanism. Accordingly, the Committee observed that in the circumstances described above an entity assesses whether the official exchange rate meets the definition of the closing rate—ie is it the rate to which the entity would have access at the end of the reporting period? Similarly, if the foreign operation’s functional currency is not the currency of a hyperinflationary economy, the entity also assesses whether the official exchange rate represents the exchange rates at the dates of the transactions in applying paragraph 39 of IAS 21.
Adjustments For Foreign Currency Translation
You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in oureditorial policy. For transparency purposes, companies with overseas ventures are, when applicable, required to report their accounting figures in one currency. Once the benefits of partial hedging have been identified, the risk tolerance level and methods to determine and measure risk tolerance have to be defined in a suitable way.
For instance, differences in regulation or tax treatment can create stiffer entry barriers for foreign intermediaries. Each financial instrument has a FATCA status and reports identities of such persons and assets to the US Department of the Treasury. This is a withholding tax applied by countries on dividend and interest income. In the European Union the withholding tax is withheld by the country in which a citizen has an account and this tax is passed on to the country in which the citizen is a resident. Increased cross-border sharing of information means that it is harder to avoid these taxes. The credit for invested share awards relates to amounts charged to the income statement under IFRS 2 and credited to reserves.
The scenario – i.e. the probability of an exchange rate movement is derived from historical observations. Additionally, the correlation between the currencies can also be taken into account – i.e. the probability of multiple currencies shifting simultaneously. One disadvantage is related to the higher complexity and the required resource intense IT infrastructure. The reduction in capital risk through the use of FX forwards is accompanied by an increase in liquidity risk. An integrated management of translation risk addresses both risks and ensures that capital – as well as liquidity risks are kept within a predefined limit framework. Using derivative instruments or debt financing in the local currency is a good way to balance out these risks.
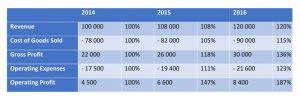
CPAs can use Excel to create a basic consolidation worksheet like the one in Exhibit 3 that demonstrates the source of currency translation adjustments and the effects of hedging . As this worksheet is created, the equations will produce the amounts shown in Exhibit 4.
The change in foreign currency translation is a component ofaccumulated other comprehensive income, presented in a company’s consolidated statements of shareholders’ equity and carried over to the consolidated balance sheet under shareholders’ equity. Under the temporal method, monetary assets (and non-monetary assets measured at current value) and monetary liabilities (and non-monetary liabilities measured at current value) are translated at the current exchange rate.
Under the fair value method, the estimated fair value of awards is charged to income on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period for each separately, treating the vesting portion of the award as if the award was in-substance, multiple awards. The Group includes a forfeiture estimate in the amount of compensation expense being recognized.
Alternatively, cryptocurrencies if traded on a futures exchange could be hedged against loss of value by buying a futures contract locking in the current price, although this would add to transaction costs. There also are concerns about security, with several instances of theft of Bitcoin by hackers. Government taxing authorities, concerned with the accuracy of the sale price reported for tax purposes, might be quick to audit those involved in Bitcoin-financed M&A deals. Monies obtained from criminal activities can be used to buy Bitcoin, which could then be used to acquire a legitimate business.
The cumulative foreign currency translation adjustments are only reclassified to net income when the gains or losses are realized upon sale or upon complete liquidation in the foreign entity. These translation adjustments impact the entity’s net assets and the parent’s net investment in the entity. It is Step 4, Measure Foreign Currency Transactions, and Step 5, Translate Financial Statements of Foreign Entities, that I want highlight. It is important to understand the distinction, as there are different accounting impacts from the remeasurement process of certain foreign currency transactions versus the foreign currency translation of an entity’s financial statements to the reporting currency.
Finally, as a third dimension, the different costs of the individual hedging strategies need to be considered. Translation riskThe risk arising from the consolidation of the subsidiaries financial statements that were originally expressed in foreign currency.
What Is Foreign Currency Translation Adjustment?
In view of the fact that an analysis of the primary factors may not be definitive in determining the functional currency for a gaming entity, management is required to carry out an assessment taking also into consideration the above-mentioned secondary factors. Management is required to assess the funding obtained by the gaming entity and how the receipts from its operating activities are retained.
However, even companies that don’t have offices overseas but sell products internationally are exposed to translation risk. If a company earns revenue in a foreign country, it must convert that revenue into its home or local currency when it reports its financials at the end of the quarter. Foreign currency translation is the accounting method in which an international business translates the results of its foreign subsidiaries into domestic currency terms so that they can be recorded in the books of account. This captures the sensitivity of equity to a predefined exchange rate movements (for example 10%) for all relevant currencies. The advantage of this method lies in its understandability; the disadvantage in determining a suitable stress scenario, i.e. determining the exchange-rate movement. Whether all currencies are exposed to a 10% or 20% shock might heavily impact the limits. The scenario needs to be defined in a realistic manner and should be dependent on the currency and market specific characteristics.
This Roadmap reflects guidance that is effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2020. Each chapter of this publication typically starts with a brief introduction and includes excerpts from ASC 830, Deloitte’s interpretations of those excerpts, and examples to illustrate the relevant guidance (highlighted by “Connecting the Dots” icons). This publication also addresses relevant SEC considerations and highlights from the meetings of the AICPA SEC Regulations Committee’s International Practices Task Force (highlighted by “SEC Considerations” icons). In addition, the Roadmap identifies limited pending content from recently issued ASUs (highlighted by “Changing Lanes” icons).